Highly Integrated VRM for data center applications
 Designed by Jiawei
Designed by JiaweiData center has emerged as a critical infrastructure supporting the seamless operation of the digital era. At the load point of data center, the power requirements for high-performance processors are rapidly increasing, characterized by high current and low logic voltage. Consequently, the conventional power architecture based on a 12V bus is no longer sufficient. To tackle this challenge, a new generation 48V bus architecture has been proposed. This high-voltage architecture offers significant improvements in overall efficiency by reducing bus-bar conduction losses and minimizing the number of power conversion stages.
Meanwhile, the adoption of a 48V architecture brings forth new challenges in achieving optimal design for voltage regulator modules (VRMs).
High voltage conversion ratio (typically 48:1)
Low load voltage and Ultra high load current (<1V & >1000A)
High power density (limited area of motherboard)
Wide bus voltage (40V-60V)
This project focus on the optimal design for 48V VRMs to meet the above requirements:
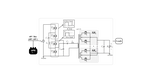
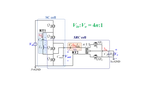
Novel topologies which combine switched-capacitor and LLC/SRC converters to reduced the turns ratio and switch rating.
Operating the converter at its resonant frequency as a dc transformer (DCX) to achieve optimal efficiency.
Proper control methods to achieve voltage regulation.
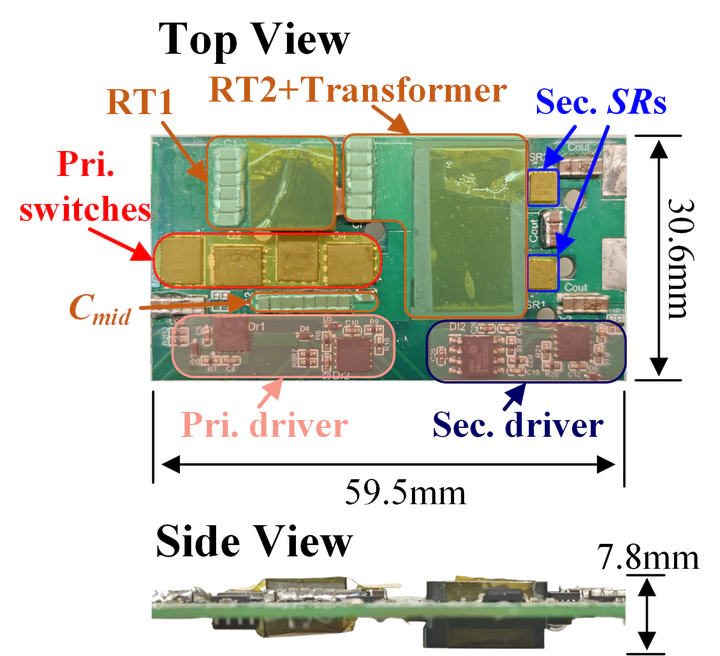
Improve the power density by less-magnetics or integrated-magnetics.